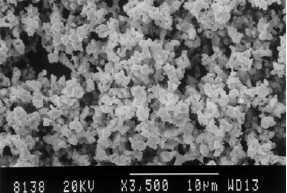
Chemical composition:
| Elements | TaC | TaC : NbC | TaC : NbC | TaC : NbC | TaC : NbC | TaC : NbC | TaC : NbC | TaC : NbC | NbC |
| 100 | 90 : 10(9:1) | 80 : 20(8:2) | 75 : 25 | 70 : 30(7:3) | 60 : 40(6:4) | 50 : 50(5:5) | 2 : 1 | 100 | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |
| Ta | Balance | 83.2- 85.2 | 73.8- 75.8 | 69.4 - 71.4 | 64.8- 66.6 | 55.1- 57.1 | 45.8- 47.8 | 58.3- 58.7 | 1.00 max |
| Nb | 0.250 max | 8.20- 9.60 | 16.7- 18.7 | 21.0 - 23.0 | 25.7- 27.5 | 34.4- 36.4 | 43.3- 45.3 | 25.8- 26.0 | Balance |
| Carbon Total | 6.10 - 6.30 | 6.5 - 6.90 | 7.00- 7.40 | 7.35 - 7.65 | 7.50- 7.90 | 8.00- 8.40 | 8.50- 8.90 | 7.70- 8.10 | 11.0- 11.4 |
| or Carbon Total is included in the following ratio : | |||||||||
| TaC | 99.5 min | 89.7- 92.1 | 80.8- 83.2 | 76.75 - 79.05 | 72.3- 74.5 | 63.1- 65.5 | 54.3- 56.7 | 66.2- 66.6 | 1.00 max |
| NbC | 0.250 max | 14.7- 16.5 | 23.7- 26.1 | 28.35 - 30.65 | 33.2- 35.4 | 42.4- 44.8 | 51.8- 54.2 | 33.5- 33.9 | 99.00 min |
| Carbon Total | included | included | included | included | included | included | included | included | included |
| Carbon Free | 0.150 max | 0.150 max | 0.150 max | 0.150 max | 0.150 max | 0.150 max | 0.150 max | 0.150 max | 0.150 max |
| Al | 0.010 max | 0.010 max | 0.020 max | ||||||
| Ca | 0.020 max | 0.010 max | 0.020 max | ||||||
| Fe | 0.100 max | 0.100 max | 0.150 max | ||||||
| K | 0.002 max | 0.002 max | / | ||||||
| N | 0.050 max | 0.050 max | 0.050 max | ||||||
| Na | 0.002 max | 0.002 max | / | ||||||
| O* | 0.250 max | 0.250 max | 0.250 max | ||||||
| S | 0.010 max | 0.010 max | 0.010 max | ||||||
| Si | 0.010 max | 0.010 max | 0.010 max | ||||||
| Ti | 0.010 max | 0.010 max | 0.010 max | ||||||
| W | 0.010 max | 0.010 max | 0.010 max | ||||||
| FSSS Size | Fine size | 0.8 - 1.0 micron | O 0.35%Max | ||||||
| Standard size | 1.0 - 2.0 micron | O 0.25%Max | |||||||
| coarse size | 2.0 - 3.0 micron | O 0.20%Max | |||||||
Appearance: In powder with yellow-brown color.
Application : Tantalum Carbide (TaC) and Niobium Tantalum Carbide (NbTaC) are used as additives mainly for P-type cutting tools and cermets because of the beneficial effect on hot hardness and toughness. Therefore these products are homogeneous mixed crystals with
high purity and narrow particle size distribution. Tantalum Carbide (TaC) and Tantalum Niobium Carbide (TaNbC) are usually used as an additive to *WC-Co ready-to-press (Tungsten-Carbide-Cobalt RTP) grade powders in order to enhance the physical properties of the sintered structure of hardmetals and alloys. TaC and TaNbC are frequently used in steel cutting grade powder attritions to maintain structure edge strength at high temperatures. In addition, TaC can be used as a grain growth inhibitor preventing the formation of large grains and increasing the hardness of the sintered part.
(* Tungsten Carbide powder (WC or WCP) is produced by carburization in a hydrogen atmosphere with a mixture of tungsten metal powder and pure black carbon, which is used to manufacture Cemented Tungsten Carbide - Cutting Tools, Wear Parts, Roll & Die, Diamond Tools, Mining Tools etc.)
Tantalum carbide is made by carburizing either pure tantalum powders or tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5). The four most important hard carbides for the production of cobalt-cemented (hard metal) carbide compositions are tungsten carbide (WC or WCP), and the cubic carbides titanium carbide (TiC), tantalum carbide (TaC), and niobium carbide (NbC). Of these, tungsten carbide is of paramount importance, in most cases forming a foundation-alloy to which smaller quantities of the cubic carbides are added to affect changes in metalcutting insert and other tool properties. In cemented carbide compositions for machining applications, preformed binary and ternary solid solutions (mixed crystals), made up of the primary carbides and based on the solven powers of the cubic carbides for WC, comprise important portions of the hard phases in cutting-insert microstructures. WC–TiC and WC–TiC–TaC(NbC) are of great importance among carbide solid solutions. WC, essentially unalloyed, is the paramount hard phase in metal-cutting tools for short-chipping materials, forming tools, and in tools used by the mineral, transportation, and construction industries. Auxiliary hard carbides of chromium, molybdenum, vanadium, hafnium, and zirconium are used to achieve secondary property enhancement. In general, the hard carbides are produced by reaction of elementary carbon or hydrocarbons and metals and metal compounds at high temperatures. Methods include carburization by thermal diffusion, by menstruum process, by thermochemical reaction, by reduction of metal halides and, to a minor extent, by fusion.
Typical size: 0.7 micron, 0.8 micron, 1.0-1.3 micron, 1.2 micron max. , 1.5 micron max.
Trade name: Tantalum carbide, tantal carbide, tac, tant carbide, ta carbide, cemented carbide powder, cemented carbide additive, hard alloy additive, tantalum alloy additive, tungsten carbide powder+cobalt powder+niobium carbide powder+tantalum carbide powder ready-to-press powder, etc.,